7 Wastes of Lean Manufacturing | The market competition is one of the biggest challenges for any business.
In modern business concepts, most of businesses are adopting various techniques and ideas to making lean the manufacturing process, to increase the profits by minimizing costs of processes. As we know, in the manufacturing processes – there are lot of factors and challenges are associated with processes.
So, now the question is what to do for eliminate these challenges and issues to reduce the costs and maintain the quality of product. The state answer is Lean manufacturing.
“Now days, the business concept is shifting from profit to customer satisfaction”.
However, customer satisfaction is one of the important sides of coin that business needs to put at prime objective, along with product costs and internal affairs are associated. Hence, the business should appreciate conduct the manufacturing processes to control over the cost with high quality of product.
What is lean Manufacturing?
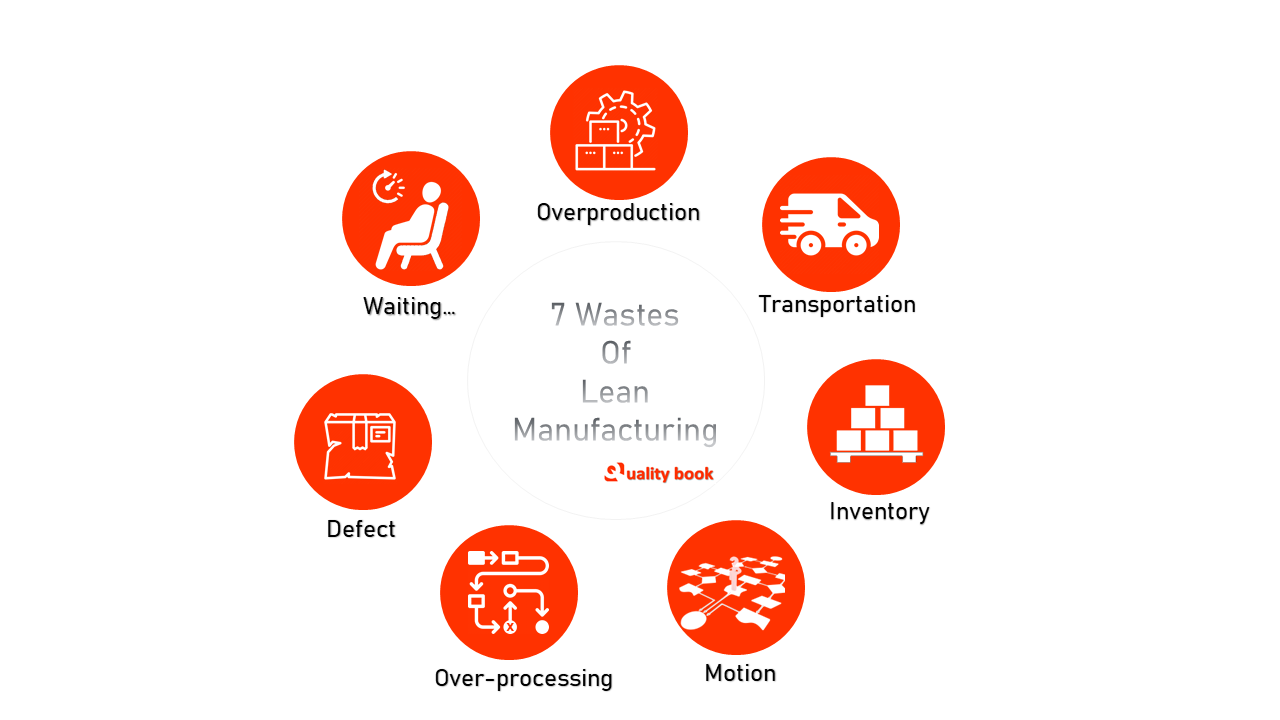
The philosophy designed for manufacturing that helpfully increase efficiency of resources, and even productivity as well. Moreover, it may help to reduces the wastage that generates from the various manufacturing processes. The lean manufacturing having a technique that makes easier to identify wastes. There are actually seven major wastes are identified in lean manufacturing method. Theses 7 Wastes of Lean Manufacturing are also called “Seven Muda”
7 Wastes of Lean Manufacturing [ Seven Muda]
- 1 » Overproduction
- 2 » Transportation [Unnecessary relocation]
- 3 » Inventory [Excess Reserves] ⁘ Examples ⁘ Consequences ⁘ How to fix?
- 4 » Motion [Unnecessary movements] ⁘ Examples ⁘ Consequences ⁘ How to fix?
- 5 » Defects ⁘ Reasons ⁘ Consequences ⁘ Examples ⁘ How to fix?
- 6 » Over-processing [Unnecessary operations] ⁘ Reasons ⁘ Consequences ⁘ How to fix?
- 7 » Waiting [Loss of time] ⁘ Reasons ⁘ Consequences ⁘ How to fix?
- 8 » Conclusion
The concept focus on identifying and eliminate the losses by approaching to enhance efficiency of business processes. However, it is now days being best practices to identifying further wastes that associates to processes. Typically, these above seven wastes are common in any kind of segment of industries.
The ” 7 Wastes of Lean Manufacturing ” is methodical procedure to reduce over pre-identified wastes set by lean manufacturing philosophy. It is helps to reduce the wastes of production, enhance efficiency and productivity of resources, control over costs and maintain product quality.
Usually, the question is raised when you refer about these losses! Why it is necessary to eliminate it immediately from the processes?
Because:
- The wastes are added to the cost of manufacturing unnecessarily which customer not really wants. These unexpected costs are loss for the business.
- These are also enhancing the payback time period of investments of business.
- It is also visibly lead to decrease in the motivation of workers.
For businesses:
It is necessary to continuously identify, track and eliminate the wastes and distinguish it immediately.
“The wastes may be parts of manufacturing processes, for which all the associated resources of business are used, however which do not create appreciate values.”
Hence, these hidden wastes are worst enemies – when you rationalize processes – you may realize that.
Overproduction : (1)
Overproduction Waste occurs when we produce more than we need of any product:
We produce.
Combine parts of a larger product, or
Moving from one place to another,
Overproduction is actually producing in excess of the anticipated, realized, or customer demand.
For any type of product in a manufacturing facility, its systematic plan is first formulating, then step by step for all the remaining processes, the entire production process for that product and all the resources required for that product are reconfigured. This process is usual for all kinds of manufacturing processes.
But, if at the outset, i.e., the plan itself is flawed then naturally it has a direct impact on the product, as well production.
In particular the following are the main reasons responsible for overproduction:
- Mis-planning of production: The cause of this type arises when there are errors and defects in the planning of traditional or specialized types of production processes.
- Production resources are not reconfigured: As you know, for each product, the process and configuration of the product is different, and the resources used in it also have to be planned properly. But if all or any of the resources are not properly reconfigured. This can have serious consequences for production.
- Redundant Hardware: In manufacturing sectors, judicious use of equipment, machinery, and other resources is essential. So, by using redundant resources and processing, the processing load increases that can be results in wastes.
The main reasons for this are lack of planning, long turnaround times or inadequate contact with customers. Which creates a barrier to understanding the ever-changing circumstances and changing needs of the customers. This type of waste in particular “increases the duration of the production cycle”.
Overproduction is actually quite deadly.
Because:
Cost of production of goods increases.
Storage and maintenance costs are incurred.
Wastes space and time.
Wastes are estimated as the sum of the costs = unclaimed products + The cost of its storage
Therefore, it is necessary to remove such wastes from the production processes in a timely manner, which must be properly planned to get the results of the right products.
Transportation [Unnecessary relocation] : (2)
This is one of the important wastes that needs to eliminate from the manufacturing processes. Typically, unnecessary transportation can be consequence of irrational re-location of manufacturing equipment.
“In terms of manufacturing, transporting anything that associated in manufacturing processes that direct impact on product / processes are move unnecessarily one place to another is calls transporting waste.”
Usually in multi-stage manufacturing, it is obvious that materials as well personnel are move from process to process or even department to department. Moreover, it is consumed time & space along with equipment such as conveyors, forklifts, trolly, trucks etc., to move the things to another process. This entire process actually does not add any value to the product. Hence, this may call “Muda Costs” for the business.
Transportation wastes are estimated as sum of the costs =
Moving resources moving costs from one operation to another
+
Value of defective product + in case any defects occurred during movement.
The best solution to eliminate the possibilities of transportation by conducting some basic steps to modify or create possible diagram of plant. Try to minimize the physical distance for materials and resources. Still make sure the manufacturing process flow match with process flow where each potential movement consume minimum time and space.
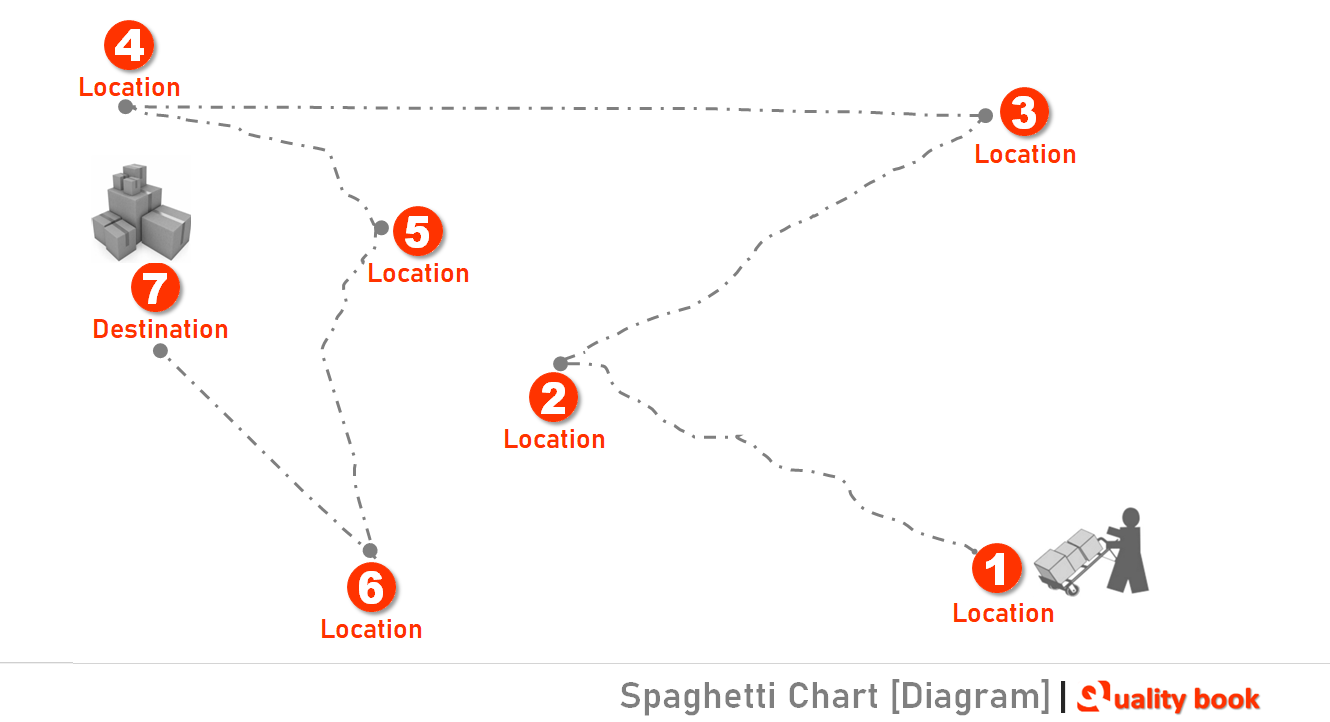
To understand your manufacturing process and its transportation, you can use spaghetti chart to trace the paths of each transportation of the materials and resource, to identify opportunities for further improvements.
Inventory [Excess Reserves] : (3)
Any kind of excess inventory can be bringing with it a host of serious quality problems. Either excess inventory of the raw materials, consumable goods or even finished products may cause the lead time incrementalist. As result serious damage of business reputation in market.
The usual reason of generated excessive inventory is consequence of overproduction, and entail with it the appearance of some wastes such as transportation and associated costs.
“Excess inventory always causes moral aging of products.” Talking from an economic point of view – after all the production costs and resources have been used up, there remains fixed money in the form of unfinished products at various stages of the production process. Beyond which the business has to bear the cost of transportation and storage.
Examples of excess stock in production
- When manufacturing processes produce very large lots, it is likely that stock of goods accumulates at various points in the production process.
- Simply and directly, when there is a lack of space to store goods across production locations, it can be considered an example of overstocking in production.
- Irregularity in the supply of materials for any production process is a sign of excess stock in the production process.
- Even though the actual quantity of the final product is as usual, if there is a need for reinsurance in the plans and processes, it should be considered to be overstocked in the product.
Consequences
- In economic terms, most of the business’s funds will be frozen, which are mainly invested in raw materials, consumables, etc.
- It is clear that when there is excess inventory in production processes, there are hidden problems in those processes. Which can be seen directly on product quality, goods handling, process cycle, plans etc.
- Generally, when excess inventory exists in production areas, the production process becomes disrupted, and problems arise in cleaning those areas.
- It is obvious that the increase in inventory increases the extent of equipment changes and new technology, thereby attracting loss/decrease in product liquidity and additional labor.
How to fix?
- While planning the production the lot/batch quantity of each order should be limited.
- Each order should be tracked according to the production processes, so that there is no accumulation of goods at one location.
- Before decommissioning old equipment check availability of spare parts and required components in store.
- By analyzing the turnover in the warehouses, it can be known that the quantity does not exceed the limit, right?
Motion [Unnecessary movements] : (4) 7 Wastes of Lean Manufacturing
In any manufacturing facility, this type of waste arises when processes are unsystematic and the goods associated with the processes are kept in disarray. This damage is hopefully avoidable. Which is considered to increase the time of the processes.
“Unnecessary movement is the waste caused by personnel’s illogical arrangement of materials and lost time in searching for items.”
When a task is performed by any employee that does not add value to the activity, and these processes only waste time, such activities must be reduced or eliminated. Such as an employee searching for unnecessary files or papers during working hours, or searching for an employee’s tools or objects.
Examples of unnecessary movement in production
- When there is a “lack of standardization of work” in a manufacturing sector, it is likely that this type of conflict will arise.
- Mixing of used goods and materials can also cause generation of this type of waste.
- The layout of any work area, such as a mechanical tool cabinet, consumables rack, tool storage area, or even a computer folder, creates “illogical order of work” or “inconvenient arrangement”.
- It is also necessary that the manager of any production should ensure that the equipment provided to the employees is suitable for their tasks or not, it is a loss.
Consequences
- This waste can cause fatigue, emotional stress, job dissatisfaction, injuries and occupational diseases among employees.
- Lack of judicious use of personnel and resources can lead to reduction in productivity.
- Searching for necessary information, details, and necessary tools wastes time.
- There is an increase in unreasoned transactions, which do not add value.
How to fix?
- Involvement of employees is very important for successful completion of any work in production areas, so to “standardize work” involve employees department wise.
- Optimizing the working area as well as the production processes.
- It is very important that all employees working in production areas should be given advanced training from time to time.
This waste is closely related to wastage of time, so if it is not removed in time, it has serious consequences. In particular, wasted time and downtime deprive most processes of efficiency. Which creates more trouble for employees. So, to eliminate this type, draw realistic diagrams to understand “how the process flows” and find solutions.
Defects : (5)
Product defects are considered to be the biggest loss in any manufacturing facility, as product defects are detected especially during product quality control. By that time most of the production processes are completed. It is obvious that if all the production processes are completed then all the processing costs incurred for the product are borne by that manufacturing facility.
“Production with defects is a serious problem and loss for the production sector, so that additional costs are incurred for cleaning, control, organization of the location to eliminate the defects.”
Reasons
- The main reason for the loss can be the low qualification of the employees as well as the inadequate quality of the materials used.
- This type of waste is likely to occur if the latest techniques installed in the production areas are violated.
- When information is lacking, consequences are unclear, or discipline is lacking.
- Lack of standards for provision of information processes or lack of tools for the same.
Consequences
- Due to this loss, there is a possibility of delay in the delivery of the product to the customers.
- Defects are a serious problem, leading to increased storage of products.
- Product rework, repair or other reasons – increase in unplanned work, thereby wasting extra money. And the cost of reprinting the raw material also has to be borne
Examples
- This type of waste can also arise due to simple errors like lack of information, improper paper work, wrong format and information, errors while entering information etc.
- An example of this type of loss is the redaction of completed works and documentation thereof.
How to fix?
- First of all, the necessary standards for product quality should be established, as well as all the information that should be explained to each employee.
- Quality criteria, proper design of processes, and process organization.
- Developing and compiling uniform templates of documents / reports / analytical notes etc.
- Developing standards considering end user needs.
- Emphasis on employee training and development.
Over-processing [Unnecessary operations] : (6)
When any manufacturing sector carries out processes to produce products beyond standards or customer requirements, those unnecessary processes are considered as waste.
“Unnecessary processing on a product, additional processes that do not add value to the product and customer satisfaction, are waste for the manufacturer.”
This type of waste is produced when more processes are performed on a product than what the customer wants and is willing to pay for. These additional processes do not improve the product or process by adding features that have no value in the eyes of the customer. This is a type of information deficiency – something the manufacturer “believes the customer needs or wants”, but does not confirm with the customer.
Reasons
- When the manufacturer does not have a good understanding of what the customer wants, there are chances of implementing additional processes that are wasteful.
- Manufacturing sectors lack adequate standards for systematic production and production processes and procedures.
- Inadequacy of modern technologies is also a responsible reason.
- If the equipment, resources, and materials used in the production processes are [incompatible] with the process requirements.
- Lack of interest among the workers and supervisors attached to the production processes in correcting the errors and defects in the processes.
- Low-skilled workers are employed on critical parts of production processes.
Consequences
- When the product is not according to the requirement of the customer, then it is natural that the customer may have to work more than necessary to make it as per their requirement.
- Due to additional processes, the manufacturer has to spend additional materials and time.
How to fix?
- For process improvement and customer satisfaction, work closely with the customer, study all their needs What is the ultimate utility of the product?
- Develop an understanding of the primary and secondary qualities of the product, and discuss the same with all employees.
- Organization of conditions, places for independent control of production of parts
- To maintain complete in standard work and instruction of work for all processes of production.
This is a serious problem, the manufacturer understands that the best quality is being given to the customer, but what is the end application of the customer? if the customer has to put in more effort to make the product suitable for his product, then your product is a waste for him. So even for the manufacturer the extra and unnecessary processes are waste.
Waiting [Loss of time] : (7)
As you know, production processes in every manufacturing sector are interdependent, one process is completed and then another process starts. If the flow of these processes is not managed judiciously, it gets diverted and generates waste. I have worked in various parts of the production facility; I have seen that in the “Production Register” the supervisor writes “No Goods for Load”. This indicates that there is a wait for the process to be completed or started in the production areas.
“Waiting is a loss associate with downtime of personnel and resources.”
When you look at a process in the production areas that are waiting for something, all the employees, equipment will be seen idle and all the machinery will be in a stopped state, which is not reasonable for a manufacturer. So, it is imperative to dispose of this type of waste on time.
Reasons
- The main reason for this type of waste, which is found in large quantities, is failure in the supply of raw materials.
- Lack of information or similarity from one process to another.
- When delivery of the same goods, one department lacks coordination with another department.
- Unbalanced work of the operator of machinery, equipment or tools can also be responsible for this.
Consequences
- If employees have to wait for goods, equipment or anything else, frustration gradually spreads among them. Which in turn affects productivity.
- If the analysis is complete at the end of the quarter or year. It will be realize that, there will be a decrease in the overall performance of the production.
- In the long run the time to production a unit of output will be increase.
How to fix?
- It is very important to note instances where employees have wasted time waiting for items, and find ways to resolve such issues.
- Pareto chart to coordinate processes – Take steps to eliminate your losses by ‘load leveling production line’ using data for process cycle, as well as time taken by processes.
Conclusion
In fact, in order to eliminate any waste (7 Wastes of Lean Manufacturing). The manufacturer himself determines which methods of solving problems should be applied in a particular case. Which can be determine base on the type of activity and the problems to be solve. However, any activity becomes lifeless without the cooperation of employees.
Whenever any problem-solving procedures are carrying out. All the employees may connect with the production processes, and must participate in this campaign. Many organizations do not pay due attention to the development and improvement of the competence of their employees. However, working personnel play the first role in creating lean production and reducing losses. If the organization is on the path of improvement and uses modern methods of production management . It is necessary to take care of the organization of proper training of employees.