In this modern era, to sustain products in the market needs to use advanced manufacturing processes. Modern machinery and cost effective processes for produce quality products with low cost. but as you all know that. It’s difficult to constant manufacturing processes and sustain product quality. Because it is natural that, during the working time unexpected problems can be occurred and that kind of problems must be resolved in respective manner. Some organizations are used outmoded technique that solve the issues on temporary basis. As well those problems can be possible reoccur in processes in future.
So, needs to efficient system that eliminate the possibility of reoccur issues as well as smooth the manufacturing processes. Fortunately, we have some problem solving tools can solve the issue permanently. 8D (Eight disciplines) is one of the popular problem solving tool that in now days, organizations are adopting pleasurably. OK, so let’s see how to implement 8D in organization.
What is 8D (Eight Disciplines)?
“8D (Eight Disciplines) is problem solving tool / methodology used for correctly identified the cause of the problem, fixed and dissipate possibility of recurrence of quality problems.”
8D model is systematic approach popularly used in responding to manufacturing issues. Generally, quality team conduct eight disciplines processes for identify root causes of problem and eliminate it by appropriate actions. The 8D (Eight Discipline) model is correctly identify the cause of the problem. And apply such actions to prevent recurrence of the problem. 8D is perform as preventive and corrective action system by implement step by step process to identify potential and actual problems in processes.
Benefits of 8D (Eight Disciplines)
- The 8D method is very easy for implement in workplace as well as logical method that clearly indicate required steps of problem solution.
- The method is very popular in automotive industry, mean your customer may ask for 8D report for its own application implementation. Because it is reliable and well know problem solving tool for automotive industry.
- An excellent way of reporting non conformance to suppliers and their corrective actions.
- 8D helps to eliminate complicated issues at appropriate locations where defined the causes of the problem incorrect, lack of consequences in implementation and same problem appear again.
- The team approach works best when the problem, and its associated information is labyrinthine. Because 8D is designed and capable for special cause of problems identification and elimination.
8D (Eight Disciplines) Process Chart: Table
| WHAT RESULTS (PROCESS INDICATORS) | INPUTS | BY WHOM | HOW | OUTPUTS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| To identify and eliminate problems. And to Prevent reoccurring problems. | Notification of non-conformity products / process and products return from customer. | CFT (Cross functional team) responsible for performing 8D process. | The process carried out using qualitative analysis in the form of a case study of the 8D method. (Integrated supplementary tools) | Corrective actions and preventive actions on identified causes of problems. Assurance of not being recurrence of such problems. |
8D (Eight Disciplines) Methodology
- D0: Plan
- D1: Team Establishment
- D2: Problem Description
- D3: Containment Action
- D4: Root cause
- D5: Corrective Action
- D6: Implement and validation corrective actions
- D7: Prevent recurrence
- D8: Verify and congratulate team

The 8D (eight Disciplines) is a process for systematic introduction of quality perfection, improvement and elimination of problems. Here in this article I will show you step by step approach and using several examples of the problem solving tools. When we involve in 8D methodology and its processes using a structured method, we become very effective at identifying cause of problems, defining problems and mistakes. As well as easily establish root causes and taking actions that solve and prevent problem identifying in processes.
So, let’s see 8D (Eight Disciplines) in deep:
D0 » Plan
As you well know, whenever any problem occurring in the manufacturing processes before you must see some warning sign that indicate the problem. Which is being experience in terms of an undesirable results and can be describe using data to identify the variation as expected and actual results.
Actually, this is the preparation stage that require to be complete before starting the eight disciplines processes in organization. Generally, peoples asking what type of preparation required before 8D process? –
A deep analysis and empathetic of the issues and problems, previous experience with same issues or related issues are necessary to determine. If the eight disciplines (8D) is the correct method to be used for solving the issues.
You have to ask the questions as below as recognizing the problem:
- Describe it is new problem in organization / division? If same problem, occur previously at where? If it is new how long from it were being in process. Or it is unknown cause?
- Has it occurred before? where? and what solutions / actions are applied at on it? What is the history of this problem?
- Why it’s happened again? is there proper solutions are not applied? what causes behind it is occur again?
- What problem solving method was used? It was joint method for one or more problem? if it is separately performed what was defects remained in method?
- To consider warning sign of problems is it really looks very complex to one person cannot resolve the problem?
- To consider above points, does the problem warrant required an eight Disciplines (8D) method? if yes, why and proceed it.
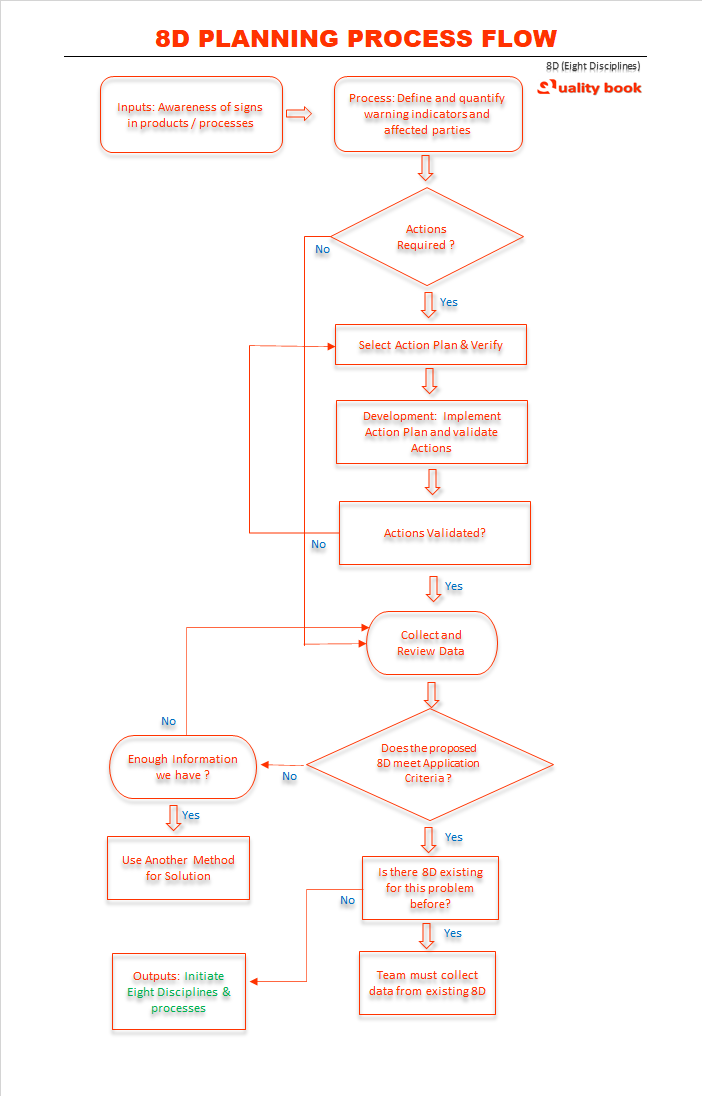
The 8D (eight disciplines) process is a team based problem solving methodology. Hence the team members must be involve for identify, action plan and eliminate issues of appropriate problem. A deeper understanding of the problem & its previous records are required to ensure if the 8D solved issues for raise issue.
D1 » Team Establishment
The team establishment is first step of the 8D (Eight Disciplines) approach. This discipline is significant stage as the eight disciplines is based on the substance of team cooperation. Establishment group of peoples called CFT (Cross Functional Team) where must each one from different department is selected by management, with the production process knowledge, product knowledge, and skill in the required technical disciplines to solve the problem and implement corrective actions.
Why team approach is important?
- CFT (Cross Functional team) build by group of peoples from different department and expertise. So any technical issues can be possible to identify, fix and eliminate problem through it.
- A Cross functional team can perform more effectively than individuals trying to solve problems.
- Cross functional team may have adequate capability to introduce proper solution of the problem.
- A group of people can discuss, focus on negative effects of actions, and can think creatively.
- Brainstorming as a group can stimulate ideas giving the team a better perspective of the problem.
A Cross functional team for eight disciplines consists of more than two people who are closely concern to the problem. Generally, involves peoples form different departments in the organization coming together to solve a problem. The skills that the team members require for this discipline to ensure the proper solution are:
- (A). Team member must knowledge of product / part / item (manufacturing processes, assembly etc.)
- (B). Team member must know the process where the problem has showed itself.
- (C). Team member must have knowledge of the customer application, technical use and end application requirements.
- (D). Team member must have skill about decision making, communication skill, and analysis of the processes and data related to manufacturing processes.
How to define team role & responsibility?
Usually, every team must have leader, here the same team leader has an important role to establish procedures and implement actions accordingly. The team leader must prepare a list defining the team structure as eight disciplines concern. the list is also important to establish role & responsibility in 8D processes. Every team member has its own importance in 8D methodology. Because every single member comes with different expertise. Hence to solve problem multifunction conception and views helpful for appropriate issues.
The role and responsibilities of the individual team member must have allocate by the team and will involve some of the points are:
Data collection and analysis, experimentation, decision making processes, modelling managing resources, planning and implementation of action plans, action plan verification and validation, communications etc.
The common processes and requirements for the 8D processes needed to contribute to the problem solving effort.
D2 » Problem Description
Problem description is a second stage designate for deep into the problem & getting a more complete information and sophisticated understanding of the problem. The problem description indicates, problem clearly identify and the eight discipline problem solving planner activities to take as much actual information as possible. Which organizes the first analysis perform in the problem solving process. You have to describe problem accurately in this stage, clear designed information is foundation to further steps of analysis.
The process of this discipline as below:
Describe The Problem Process Flow: Table
| FLOW DETAILS |
|---|
| Establish the data base that currently exists for the problem description. At this stage of the problem solving process, you must look to provide brief data about the problem and determine the exact nature of the problem. |
| Prepare a process flow diagram for all product stages. |
| Collect current and historical data as needed to further quantify the problem. Previous eight disciplines record helpful to accurately describe. |
| The problem be subdivided. |
| Describe the problem in terms of an operational definition. |
| Convention the customer to ensure correct problem description. if the problem description different from the customer or supplier explanation, both shall be documented and recognized accordingly. |
| Have the extent and the distribution of the problem been established for all stratification factors. |
| Established by determining : Who, What, When, Where, How and How much huge and uses the is / is not form to drive this part of the process. |
| Prepare problem description. |
A problem description is the results of a practice that uses the is / is not method to magnify the problem statement. The location and nature of the problem have to be describe along with its impacts. Another very important analyzing results of information. To ensure that the problem involves is recurrent or whether it could occur on particular process or product.
See table below help for better understanding:
Describe the problem with Is / Is Not Method: Table
| FUNCTION WORD | IS | IS NOT |
|---|---|---|
Who |
|
|
What |
|
|
Why |
|
|
Where |
|
|
When |
|
|
How much / Many |
|
|
When the describing the problem with 5W + 2H (Who, What, Why, Where, When, how, how many / much) method should be use. Where you get the answered thoroughly and systematically by the questions.
See picture below for problem analysis worksheet:
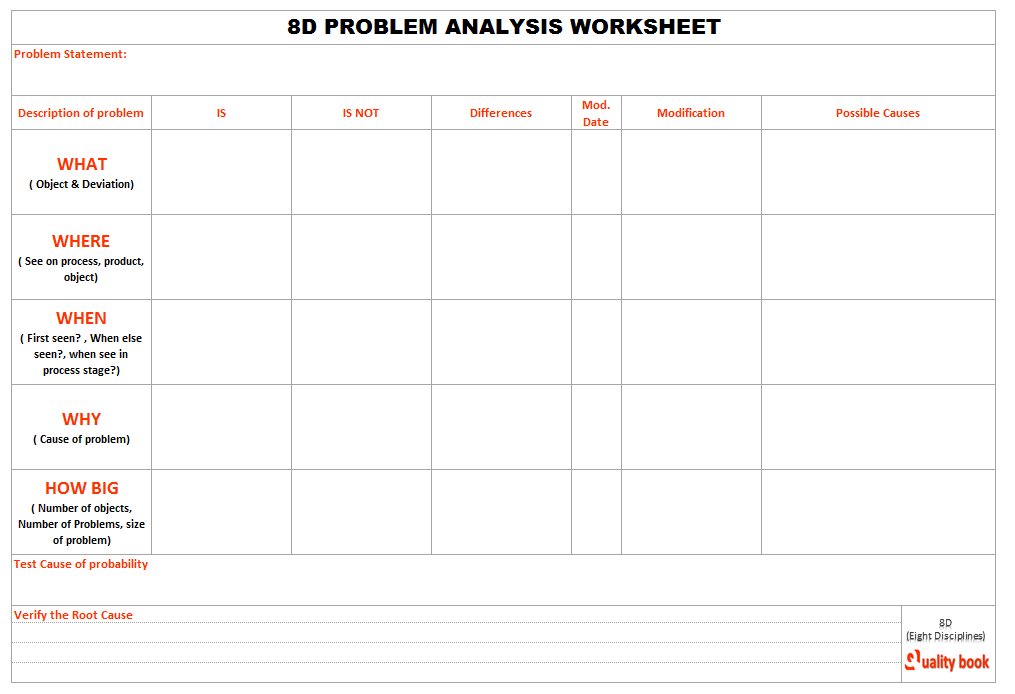
Remember that, you have to specified problem statement been defined, and you have get to know for certain why that is occurring. So Is / Is not analysis must been perform for it. You have to also verify that the similar parts / components displayed the same problem? current process flow identified? does this process flow represent a change.
Once you get the answer you can collect the data and analyze it. The information you collected are evaluated for potential root causes, and identify physical evidence of the problem. The problem description been reviewed for completeness with 8D (Eight disciplines) customer and affected parties, and document the activities.
D3 » Containment Action
This is the stage where are taken correct containment action to prevent escalation of the problem. Or at the worst delivering non-conforming product to the customer. You have to describe the containment action plan to put in place in order to eliminate the effects of the problem. In this stage, immediate correction action should be carrying out in the shortest time possible. The main objective of the implement interim actions / containment actions to isolate issues from parties while a permanent solution is being develop and implement.
Why containment action required?
- When the cross functional team working on identification of the root causes of problem, collecting information and other related processes might possible some defective product produced by manufacturing in tenure. So, it is extremely important containment actions on this condition at appropriate locations.
- To ensure the customer has minimal or no impact felt as a results of the problem identified, as well prevent these defective products from getting the customer.
- In case of any defective lot / product reached to customer, it may not comply requirements to end application, hence customer will claim and complaints as results customer dissatisfaction.
- Due to immediate actions, the similar products and processes must be verified and ensure the risk levels are minimum or not evident.
Through PDCA Cycle
Plan » Prepare the most effective containment action plan and implementation including verifying the containment action effectiveness and concerned activities such as work instructions, resources and equipment available.
Do » The plan must execute as containment action plan prepared, and ensure that the actions should be clearly communicated at processes and management levels.
Check » It is cross function team responsibility that every containment actions prepared during the planning section must be implemented exactly accordingly and ensure that it may continue to be effective. One of the important activity of this section is to verify and ensure that. The activities must not any other side effects raise as a result of the containment actions.
Act » Take the actions to ensure containment action are effective and sustained with all manufacturing and supporting processes. Take the questioners and get the feedback from internal and external customers to implement and make sure is there further containment actions or correction required to rectify other issues.
8D – Containment actions checklist

8D containment action points:
- A. ✓ Have the containment measures been verified to work?
- B. ✓ Are the interim containment measurements appropriate? are they effective?
- C. ✓ Has the adverse effect recorded of the containment measures? it is tested to ensure that no further problems are being created?
- D. ✓ Have the appropriate department been involved in the planning of this decision?
- E. ✓ Are the actual surplus costs of the control measures knowing? Have they been verified that they are means it?
- F. ✓ Containment actions could be implemented at all the effected or identified places? Is there any other location identified for the same issue?
- G. ✓ Based on the criteria established, does the containment actions provide the best balance of benefits and risks?
D4 » Root cause
On this stage in Eight disciplines (8D) problem solving process, needs to establish and describing the root causes of a problem is the core of this disciplines. And you will have appraise the team structure and configuration to ensure that all the right skills and experience is available for the upcoming phases or processes in the problem solving effort.
Elimination of the problem should be detecting the real cause of the problem. The objective of the explain and verify root causes is to identify all significant causes which could clarify why this problem happens. An eliminate and confirm the root cause by examine each significant cause against the describe problem and results of tested data.
For define and verify root causes you have to step out as below:
- Establish a process flow and Cause and Effect Diagram to include all the sources of variations.
- Develop a stratification cause and effect diagram, but remember that, the cause and effect diagrams used input from all team members, lack of the information of remains any points or data left, you will not get real cause.
- Establish comparative analysis, by determine critical differences between problem location and non-problem locations.
- You can also use time line analysis. Graphical / visual charts give you better understanding in most cases.
- Index the potential causes of problems by use both the process flow and cause and effect diagram.
- By using the both the tool, you can analyze the potential cause for the most likely cause.
- Determine slot of data, identify the potential cause as a root cause.
- Collect and analyze the appropriate information to identify the potential cause as a root cause.
- Specify causes that permitted the apparent warning sign to occur, are the root causes and often repressed deep in the processes. You can use the tools to help in the whole processes that is problem solving techniques are : (1) Pareto charts (2) 5 Whys analysis (3) Statistical analysis (4) Flow charts (5) Fishbone diagram (6) GR & R study (7) FMEA (8) Frequent audits (9) Fault tree Analysis (10) Brainstorming etc..
The time line is one of the important and useful tool that manage the records at time line of all events in and around the problem.
Example:
A company making steel tubes is experiencing a pits on tubes problem identified.
The significant processes / event are recorded on a time line are:
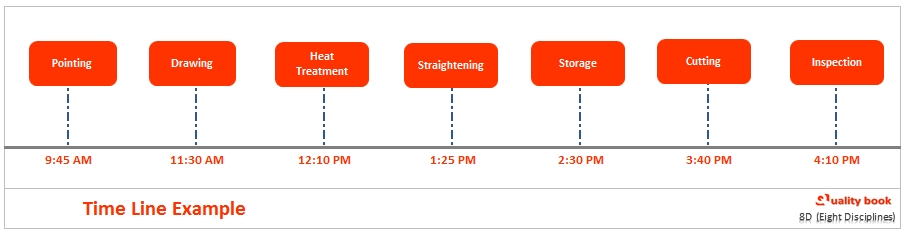
The time line helps to draw processes and events on time. Though it you can get the answer when actually the problem was first seen at which location. Now you can filter out possible causal theories later in the process by identifying what could possibly have caused the problem and what could not have caused the problem.
There are more three important stages you have to concentrate are:
(1) Develop possible causal theories (2) Establish possible root causes (3) Verify possible root causes and define and verify escape point.
You must do deeply thought about the possible causes and documents on separate media. For each of the cause you have to prepare a proper theory that describe how that the possible cause would result in the problem being experienced. You have to do write note of each ideas for develop causal theory for possible root causes.
Ask the simple question to each causal points that answered in “IS” / “IS NOT”. Does this explain the reason why the problem exists on the “IS” and not on the “IS NOT”. For separately of the possible root causes, there now requirements to be useful action to validate the possible root cause. This should be carried out in practical terms wherever possible.
D5 » Corrective Action
On the fifth stage of eight disciplines, the cross functional team must determine which corrective actions should be establishing and implement in the short period of time to ensure that the processes and product quality maintained and controlled. The corrective actions must be requirements that satisfy both the parties internal and external customers. Once the root causes are known, team concentrate on the permanent solutions, by systematic approach is needed to use the root cause analysis to establish actions for proper solution. The points that you need to focused on:
- Empathetic and defining the problem, the eight disciplines (8D) team must be able to defining the problems and implement the solution practically.
- Enclosing the effects of the problem, please note that implementation and using the program for solution must be cost effective.
- Identifying and verifying the root cause of the problem.
- Need to permanently solve the problem, and the solution must be feasible.
- Confirm the potential solutions through testing programs, and remember that the implementation program should not fail during the implement in production so, it is important the solution is a test and essential characteristic such as mistake proof and affordable.
- Verify that the solution eliminates the problem and its effects;
In fifth stage of eight disciplines, the team can introduce the additional control in the processes, and ensure that the solution is properly validated that during the implementation in running production it will not raise any unwanted issues, so trail on the small quantities first to verify the solution is effective is necessary. To ensure that the permanent corrective actions need to establish proper process flow for it, see the example process flow:
Verify Corrective Actions Process Flow: Table
| Conduct Inputs to verified root causes |
| Establish Corrective Action Decision Criteria and Re-evaluate team composition is customer represented. |
| Choose the suitable permanent corrective actions |
| Choose indicators and record baseline data, and plan corrective action feasibility using pre-production test program. |
| Record verification data |
| Has the program been solved and verified using the appropriate statistical method, if yes go ahead otherwise re-arrange the permanent corrective action plan and chose best for appropriate requirements |
| Does the customer agree that the problem has been corrected? if yes go ahead otherwise re-define the customer issues, and identify proper corrective action plan accordingly. |
| will the corrective action when implemented avoid creating problems with the customer? if yes choose verified corrective actions, otherwise follow the selection of corrective actions. |
Verify the corrective actions
It is extremely important that all the established actions and implementation plans for fix the issues must be performed to not leading any further problems. So, cross functional team must well aware of this kind of technicality and must should try out the implementation program with small part of production or small quantities first to verify its effectiveness.
Corrective actions test with pre-production with small quantity can confirm that the identified corrective actions will resolve the problem of the customer, and ensure that will do not any undesirable side effects.
Check points
- A. ✓ Check is there the criteria been establishing for selecting corrective actions? The root cause and escape point?
- B. ✓ Developing corrective actions and its implementation, is there all the resources and capability are considered?
- C. ✓ What risks are associated with the corrective action plans and implementation and how should they be managed?
- D. ✓ Can the corrective actions have implemented as per plan?
- E. ✓ What evidence do you have that this will resolve the problem at the root cause level?
- F. ✓ Does the return on investment of the corrective actions justify the cost of implementing the corrective actions? And the corrective actions passed the tests of practically, feasibility and cost effectiveness?
- G. ✓ Do you have the right team composition to proceed upcoming stage? Is there further training requiring? Have plans been generated?
Somethings that still need to confirm and ensure that corrective action is will properly works at real production. Some points that help you to re-verify the condition such as:
- (1) List and measure all of the indicators related to the program.
- (2) identify which of the indicators are most direct relation to the program.
- (3) Determine intervals to measure the problem.
- (4) identify what cross fictional team prioritized the customer / end user evaluation after the implementation.
- (5) confirm the scientific methods used to verify effectiveness etc.
D6 » Implement and validation corrective actions
On the stage of validation corrective actions, the cross functional team consists of measuring the long term effectiveness of the corrective actions. The purpose of verification of the corrective action is ensure that the actions are implemented are efficient and these are eliminated permanently through effective controls and activities that are embedded in the tasks of the process. Some indicators that you can ensure that the corrective actions are properly works:
- Test and control results display improvement
- Less Rejection or reject ppm (%) in process.
- Measurements such as dimension, units’ appearance are correct according to tolerance and specifications.
- Controls on incoming raw materials for quality improvement.
- Increased satisfaction ratio and feedbacks from customers.
The statistical tools such as process capability, histograms, control charts etc. can used to measured and verify the effectiveness of the implemented corrective actions. The cross functional team must have informed to customer about the results achieved, if the process capability submitted with the requirements the customer validates the corrective measures functional. The 8D team confirms whether the capability complies with internal manufacturing requirements, if the process capability complied the team validates the corrective action.
Checkpoints:
- A. ✓ Has an action plan been clearly defined and communicated, all the responsibilities assignment, time scope and required support determined?
- B. ✓ You have to check out, do you have necessary resources to implement the corrective action plan? The current action plan is adequate or needs complex action plan? If a complex action plan is required all the related requirements such as pert charts, Gantt charts etc., included?
- C. ✓ What are appropriate contingency actions and what will trigger it?
- D. ✓ Is there customer as well supplier’s involvement is required?
- E. ✓ The implementation of corrective actions and its related changes such as procedures or internal quality system has been done? Are there any documents such as FMEA, control plan, process flow has been documented? As well as all systems, practices, documents updated along with? Had training to support the new / changed system been developed and provided?
You can use PDCA cycle for implement this stage in manufacturing processes. The implementation of the permanent corrective action conduct to implement to verify the plan for validation of the corrective action. You can plan to withdraw containment (immediate) action as part of implementation of the corrective actions.
There is also important that each resources used in processes must be properly planned as well as all documentation, process instructions and communication implementation for corrective actions. Check that the corrective actions have been implemented and integrated into the appropriate tasks and manufacturing processes. Take the actions on any variation from the plan or expected results.
D7 » Prevent recurrence
On this stage, the cross functional team have to determine what action should be taken to prevent recurrence of the problem. You have to amend those operating systems, regular practices, management system as well as procedures to prevent recurrence of this problem and all similar issues. Because preventing recurrence is a one of the important task of problem’s solution. The general process flow of the prevent recurrent is:
- Input implemented corrective actions and validation
- Review the history / previous record of the problem.
- Analyze how this problem occurred and escaped.
- Identify affected parties and opportunities for similar problems to occur and escape
- Identify the system’s policies, practices and procedures that allowed this problem to occur and escape to the customer.
- Revise the process flow of the management or operating system.
- Analyze how similar problems could be addressed.
- Develop plans to coordinate necessary actions. And verify prevent actions.
- Develop systematic prevent recommendations to process owner.
- Identify and choose prevent actions. And implement preventive actions.
- Make the system changes to prevent recurrence.
- Verify the preventive actions are effectives? If yes, Standardize the new practices.
- Notify all personnel of the resolution actions by using failure mode effects analysis.
In this stage of the 8D (eight disciplines) cross functional team analyses whether the corrective action implemented would prevent or improve the quality of similar products and processes. To ensure the prevent recurrent of the problem, you should verify results of their actions and must validate that the results is on target. To verify the actions, you must check out below points:
Checkpoints:
- A. ✓ Has the results of the corrective action plan been verified to work? And it is validate to be on target? The solutions identify is documented, related procedures updated and changes to any affected quality system elements made?
- B. ✓ What requirements to be complete differently to prevent recurrence of the root causes and escape?
- C. ✓ Verify that all necessary controls for the particular solution are in place?
- D. ✓ How the system ensures that or indicates the requirements for a process improvement approach?
- E. ✓ Have audits been established to measure the use and effectiveness of the solution to ensure that the improvements are detained?
D8 » Verify and congratulate team
The last stage of the 8D (Eight Disciplines) Is verification of the introduced actions in previous stages are effective. It is highly recommended that verification be made by comparing the measures of the problem with outcomes from upcoming actions of material or outcomes from rejecting of next lot. Once cross functional team has complete implementation all previous stages and ensure that the actions taken in previous stages are works. All team member deserve to be congratulate as well to know that their efforts are appreciate and that the organization knows about their accomplishments.
Checkpoints:
- A. ✓ Has the 8D (Eight Disciplines) report updated and published? And 8D report related attachments retained in your historical file system?
- B. ✓ Is the 8D related all the documentation is completed and the customer has been informed of the status of 8D?
- C. ✓ The organization must have complete list of all current team members including past and all current and past team members being recognized?
- D. ✓ Were there significant contributions by individual team members? What were they? Make the separate document for it.
- E. ✓ What have you learned as individuals and as a team? And how did the organization benefit by the completion of this 8D processes?
The cross functional team must have skills and experience to be able to make progress toward as satisfactory problem resolution, and skills and experiences are base reasons for individual selection. Different skills and experiences will support to be drafted in at various stages throughout the process to get the deep understanding about the symptom of problem, root causes and resolution.
The 8D report
From beginning to end of all 8D (Eight Disciplines) processes, the single document calls 8D report is essential part once complete. Team assume that all things are complete and fix as appropriate actions for appropriate issues. This report serves as a communication tool displaying overall process of the 8D (Eight Disciplines) processes along with actions taken. So, let’s see example format of 8D report:
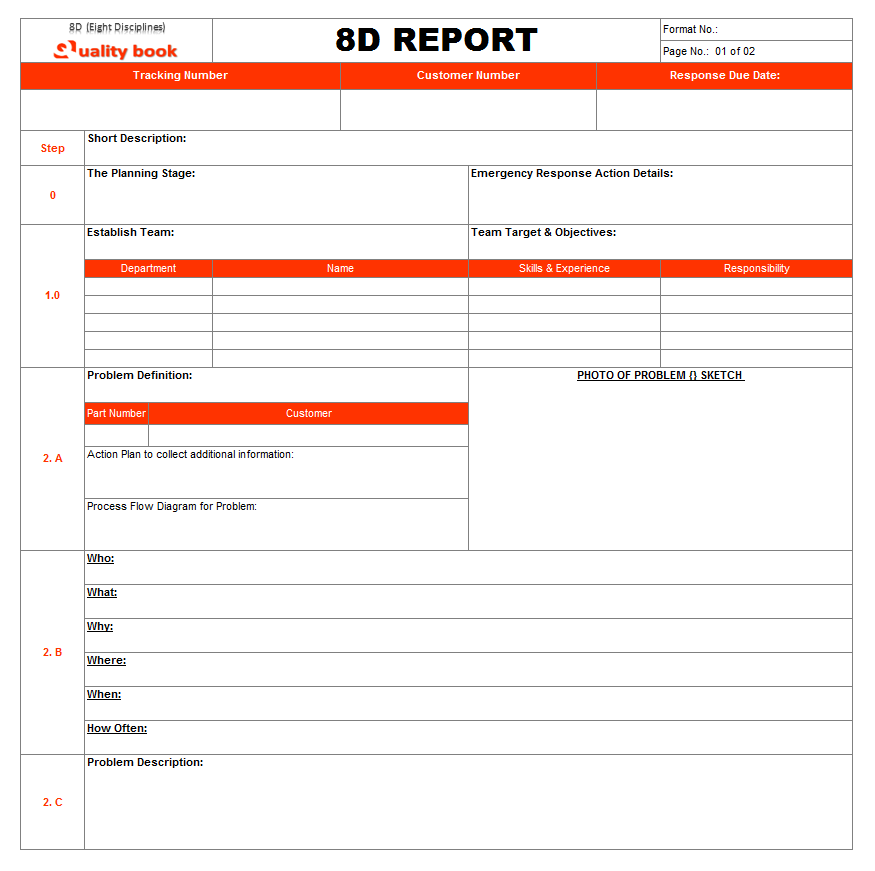
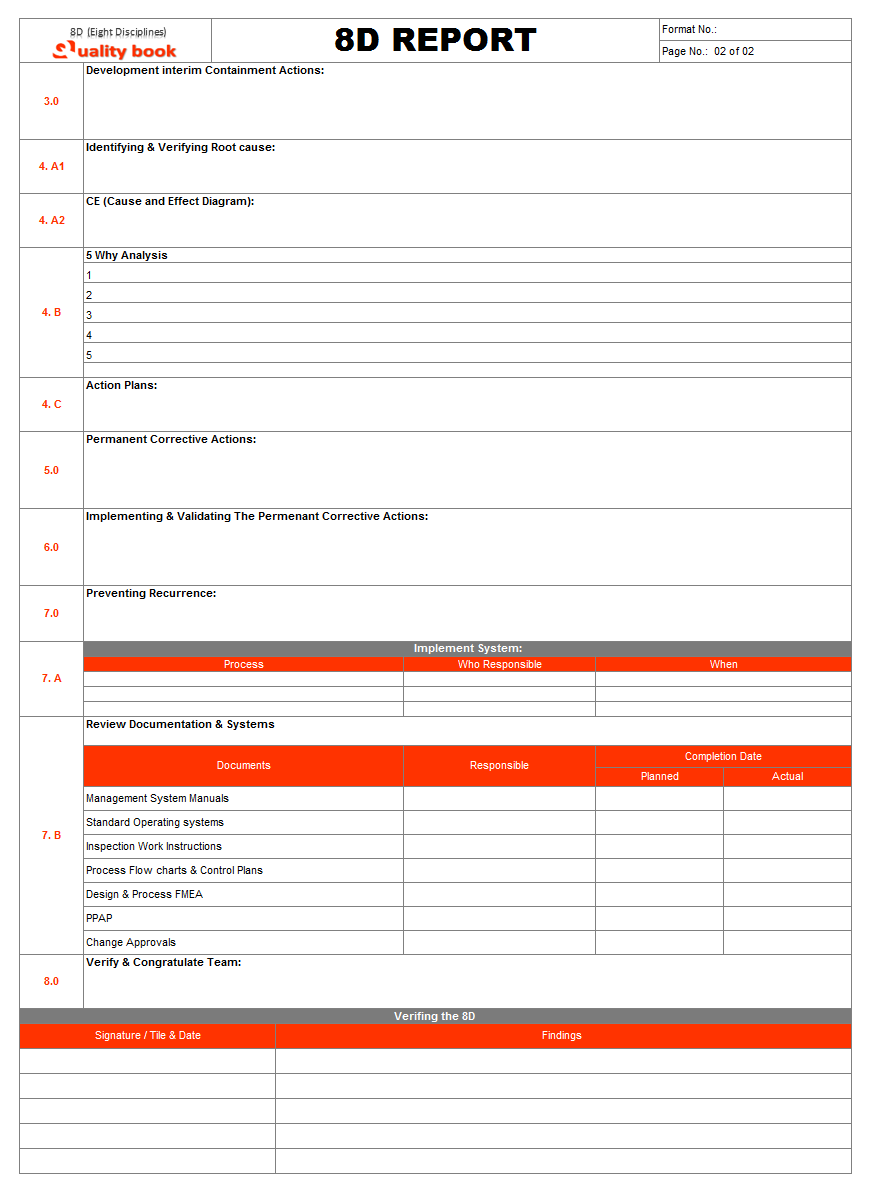
Conclusion:
When the problem has been resolve. The cross functional team should release a final document with stage wise brief description about its experiences. The 8D report give quick and better explanation of how the whole process had handling by team and also 8D serves report as a communication tool displaying overall progress of process.
We can assume that, the successful corrective actions have eliminated repetition of problems and prevention of similar issues. Further, team must ensure that corrective actions will be assess on their ability to help avoiding future problems. If we do not distinguish between major and minor problems, any issue will hold the delivery of customer and that is the reason we must have to categorize by identify systematic issues to eliminate appropriate problems.