Comprehensive quality management system production is the application of statistical methods at all stages of production that contributes to economical production to the highest degree Products. The UCP, when it develops cyclically, goes through certain stages. The cycle is called the Deming cycle, and its implementation is called the turn cycle Deming cycle.
The concept of a Deming cycle is not limited only to quality control Products, it can be extended to all management Production.
Namely, the management of any processes, including Product quality management, can be thought of as consistency passing the following important stages:
- Plan
- Implementation (DO)
- Check (CHECK)
- Correction (ACTION)
The PDCA cycle ensures the qualitative growth of services, management, and control. The Deming cycle always has not one, but several Revolutions. Implementation of this cycle by the team of specialists will improve quality Products.
With skilful implementation of the Deming cycle in the enterprise, you can expect the greatest efficiency of their work at minimal cost. Management should be organised based on six sets of measures that have proven their effectiveness.
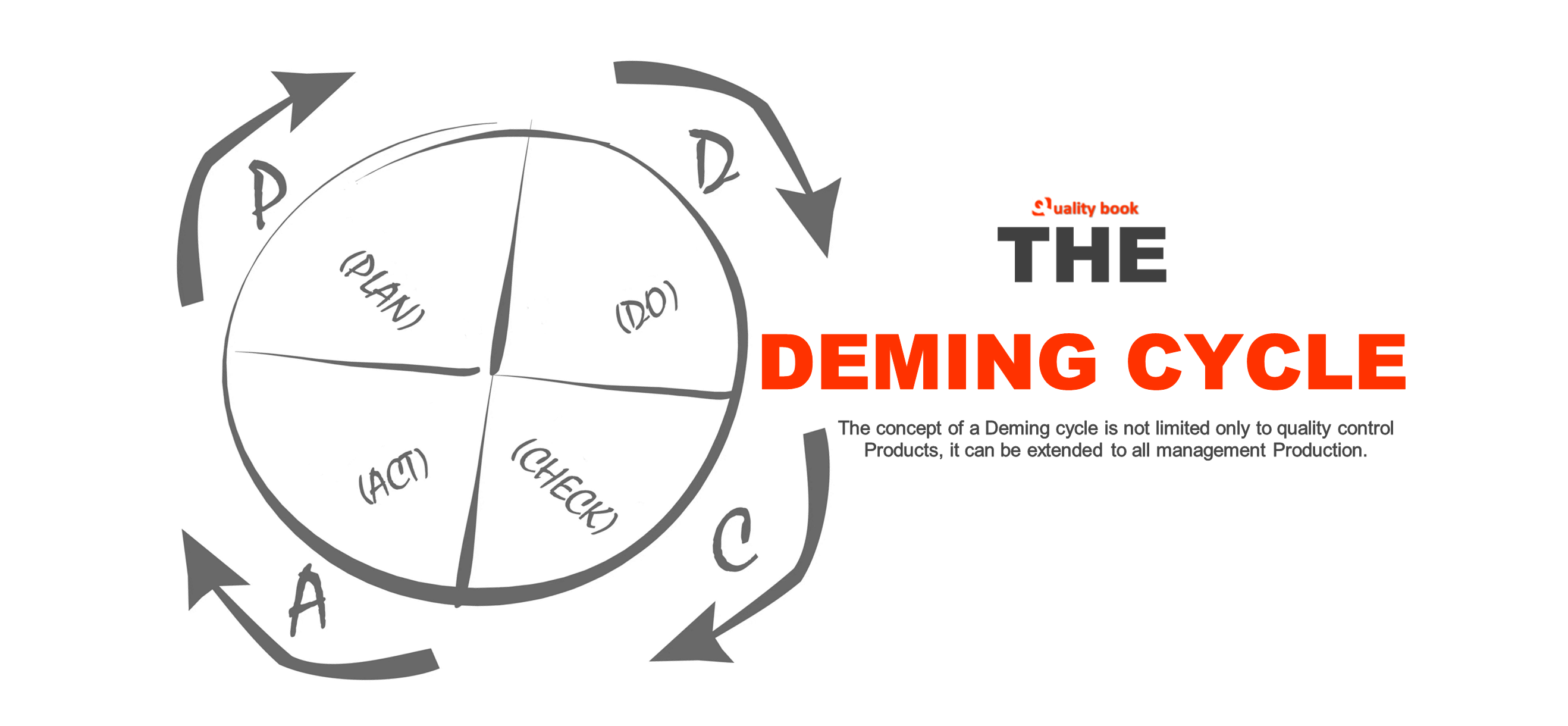
P: (PLAN)
- Definition of goals and objectives.
- Determination of ways (ways of strategies) to achieve goals. Plan Events.
- Education and training.
D: (DO)
- Execution of works.
C: (CHECK)
- Verification of the results of work.
A: (ACTION)
- Implementation of appropriate control actions. Correction.Let us dwell in detail on each complex.
P: Definition of goals and objectives
Defining the tasks, you need to install the deadline for their implementation. Tasks should be determined on the basis of standing before the firm problems and they should be defined in such a way that ensure joint action of all units.
Identify ways to achieve goals.
Getting specific metrics Quality is the goal of implementing a system. Factors and causes that form these indicators can be determined using the Ishikawa diagram. This approach helps to anticipate problems and prevent their occurrence, it is progressive governance.
During the search process, you should consult with those who are familiar with the specific process, namely the working engineers and researchers. The key to success is the decisive standardization of the obvious things and passing them on to subordinates.
Education and training
At all stages of the Deming cycle there is an urgent need for qualified and trained persons Workers. Therefore, managers are responsible for training and education. his subordinates.
Training is not limited to formal meetings the manager must teach his subordinate individually in practice. Having received education and training, a person becomes an employee for whom you can rely on and you can put on power.
D: Execution of works
You can force subordinates to execute work by giving the appropriate orders, but such a process never will proceed smoothly. Conditions are constantly changing, and orders are never will not be sure to keep up with changing conditions. for this reason, special attention should be paid to voluntary management Quality.
For example, there are many reasons to explain the failure of the defect-free manufacturing program. One of them is that the program has become a complete theorizing. forgot that every person is a person. The failure was also due to the fact that it was believed that the number of defects would be zero if strictly followed the requirements of the standards.
However, as already noted, standards and regulations are always imperfect. Only the experience and qualifications of employees help compensate for the imperfection of standards and quality.
C: Verification of the results of the work
If everything goes according to according to the tasks set and according to the requirements of the standards, there is no interference Required. But when unusual phenomena occur or are disturbed the established order must be intervened by the manager.
The purpose of control is to detect such deviations. In order to detect deviations Necessary: Check the cause first, and then perform a check of the work on it Results. First of all, it is necessary to establish whether all are controlled causative factors, every process-design, material- Technical supply, fabrication- and making sure to properly understand causal factors in accordance with the specified technical requirements.
Verification of causal factors should be entrusted to lower managers Link. Another way is to check the process or work on the results. The results also include questions related to personnel, quality, quantity, delivery time, availability raw materials, labor and equipment required to produce a unit of production and costs.
Observing the changes taking place in each of these positions, you can control the process, operation, and management.
If the results are missing or distorted, this means that in some processes something unusual is happening and there are some difficulties. The task of the manager is to be establishing the source of failures associated with causal factors.
A: Implementation of appropriate control actions
When implementing corrective, It is important to take measures to avoid the recurrence of deviations. the end of existing violations. Causative factors should be eliminated, which caused the rejection. Correction and prevention of recurring deviations- these are two different actions, including regarding the measures taken. Eliminating the causes of deviations, it is necessary to turn to the origins of the problem and accept measures to prevent their recurrence.
All these activities allow you to achieve a significant reduction in defects, and therefore an increase in quality products, reliability, and durability of the manufactured product.
Methodical
Next, we will give methods economically Efficient production of high-quality products and services. Everything the ideas belong to Dr. Deming, and are widely used in the West, in features in America.
1.Consistency goals.
Leadership’s commitment to ongoing improvements are a critical factor for maintaining enthusiasm, interest and the complicity of workers at all levels.
2.New philosophy.
A serious, radical one is expected. rethinking your views is more radical than you can imagine present. You must maintain a constant, continuous movement in the right direction towards the day when the entire company will be in the process of improving. the quality of all systems and activities.
3. Do away with addiction mass control.
Work with reliable, uniform, and High-quality materials and processes. This will affect your reputation with your current and future consumers.
4.Do away with the practice of purchasing at the cheapest price.
Aim to receive all deliveries only from one manufacturer. The goal in this case is to minimize the overall costs, not just the original ones.
5.Improve every process
Constantly look for problems in order to improve all activities and functions in the company, improve the quality and performance.
6.Put into practice training and retraining of personnel, in order to better use the capabilities of each of the Them.
7.Establish “leadership”.
It is necessary to create an environment in which employees have a genuine interest in their work, and managers help to perform it well. If workers are interested, they strive to do the work qualitatively.
8. Banish fears.
Any employee who is afraid of his superior cannot properly cooperate with nim. True collaboration allows you to achieve much more than isolated individual efforts.
9. Break down barriers.
People from different functional units should work in teams (brigades) in order to eliminate problems that may arise rather than wasting time on conflicts.
10. Give up empty slogans and calls
That require workers to work effortlessly, a new Performance levels, but say nothing about how to achieve these goals.
11. Eliminate arbitrary quantitative norms and tasks.
Replace them with support and help on the side of the superiors to achieve continuous improvements in quality and performance.
12. Empower employees to be proud of their work.
Remove barriers that rob workers and managers, depriving them of the opportunity to be proud of their work. involves annual appraisals and management methods by objectives.
13. Encourage the pursuit of education.
An organization doesn’t just need people, it needs workers who improve because of education. The source Successful advancement in achieving competitiveness is knowledge.
14. Define an Unwavering
Commitment top management to continuous improvement of quality, and performance and their commitment to implement all the principles discussed above.