MSA is an analytical assessment system. Which is defined as an experimental and mathematical method of identifying and determining the components of variation in the measurement process. This can be done to validate the measurement system for use by evaluating the accuracy and stability of the system from process to production. This analysis process has many advantages, in that it can contribute to overall process variability in production areas.
MSA – Analysis tool
“Amount of variation”, “Common sources of variation” and “Components of variation” are all considered very important for measurement system analysis. And it is necessary to review all these three important things. This system is implemented to make measurement processes efficient, and to reduce or eliminate variation. Here we map the sources of variation emphasized in the processes, which may include the following:
- About employees – operators, skill level of employees, training which directly makes a difference.
- Processes – Processes, whether of production or assembling, especially specification and testing method can be the main reason for the variation.
- Equipment – the equipment itself and its associated calibration systems, such as gauges, fixtures, test equipment
All possible sources of variation or variance must be considered during the measurement system analysis process. The use of instruments of specific quality is essential to identify the most likely sources of variation in the measurement system’s evaluation.
A measurement system analysis considers the following:
- Choosing the Right Measurements and Approach
- Measuring instrument
- Assessing Processes and Operators
- Assessment of any measurement interactions
- Calculation of measurement uncertainty of individual measuring instruments and/or measuring systems
An MSA analyzes the collection of equipment, operations, processes, software, and personnel that affect the assignment of a number to a measurement characteristic.
Why do Measurement System Analysis (MSA)?
Each production/manufacturing sector has its own set of goals, but there are some common goals that every organization seeks to achieve through measurement system analysis. accuracy, including the amount of measurement uncertainty, accuracy, repeatability and reproducibility, the stability and linearity of these quantities over time and throughout the intended range of use of the quantity measurement process, and the development of improvement plans if necessary And so on..
A competent MSA helps ensure that the information collected is accurate. It is natural that accurate and reliable information in a reliable process can prevent wasted time, labor, and spoilage.
Measurement System Analysis Glossary
Discrimination:
The smallest detectable increment between two measured values-not the same as accuracy or repeatability. Whenever you are using a gauge there is a minimum count or minimum value that you can measure with this gauge.
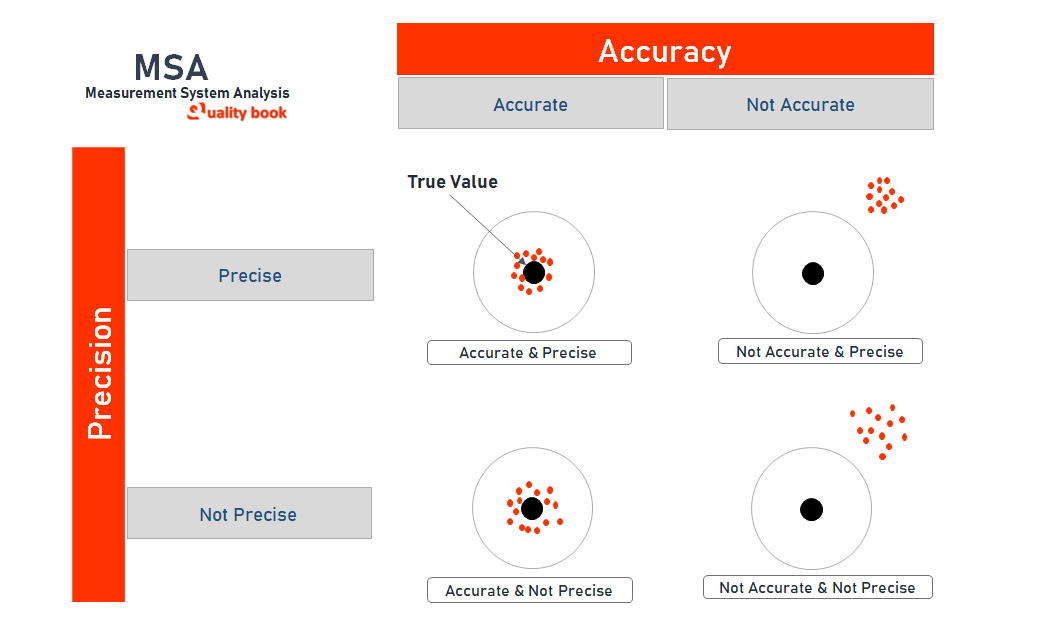
Accuracy:
It is the difference between the true meaning and the observed mean. (The true average can be obtained by using more accurate measuring equipment). The moment the mean value differs from the true mean, the system is not accurate. This is a sign of the wrong system.
Stability:
The difference in the average of at least 2 sets of measurements with a gauge over time. We measure an object at time (T1) and then after time (T2) the average values are completely different.