Modern Understanding the quality of products is based on the principle of the most complete fulfilment of requirements and wishes consumer. And this principle should be the basis of the project of any ware. The consumer of the product can be both an individual and collectives of people – enterprises, organisations, or society as a whole.
In In any case, the needs are related with the properties of the human personality. The human psyche is extremely complex, and sufficiently complete theories of needs man has not yet been built. However, Less, there are now a number of theories, describing the types and relationships needs, on the basis of which the product developer can act Confidently enough and achieve good practical results.
According to Maslow
One of the most Common theories are the theory of the hierarchy of needs scientist Abraham Maslow (Abraham Maslow). Put forward by him in the 50s years of our century. According to Maslow, there is 5 groups or levels of needs.
- Lowest Level – basic or physiological needs, such as the need for food, clothing, housing, etc., which are determined by the biological nature of man.
- Higher Level – Needs in protection from ⌠ shocks destinies, such as accidents, disease, disability, poverty, and others that may interfere with the possibility of meeting the needs of the previous level – physiological needs. An even higher level is social needs, that is, needs in communication, relationships with other People.
According to Maslow, everyone’s needs levels are related to the possibility of satisfying the needs of the previous level, and social needs are caused by the desire to satisfy security needs more fully. Next level – recognition needs, or the needs of the ⌠Ego. These are the needs in prestige, respect for others, The highest level of needs- needs for self-improvement, or development needs.
We can assume that all these species There are not only needs for the individual, but also for groups of people, including enterprises and society as a whole.
During use a number of refinements were made to the theory, The most important of which are:
According to Maslow, transition to the need of higher level occurs if the need of the previous level is satisfied 100%;
Modern psychologists believe that this percentage is less – about 70% or even less.
The hierarchy of needs of a particular person in many ways is determined by the level of development his psyche, it changes from person to person and is different in one person in different periods of his life. With the development of human psyche needs Higher level become more important than needs of a lower Level.
Quality, value, and the cost of the product
In order to satisfy human needs, the product must have certain properties, and the degree correspondence between the properties of the product and satisfied with it needs determine quality products. At the present time the measure of the quality of products is the degree of customer satisfaction with the product, Determinable value ratio and value (use value) ware:
{Quality} = {Satisfaction consumer} = {Value} / {Cost}
For the manufacturer all products free from defects that would prevent the sale of this product, have value.
The consumer, the value is only those properties of products that meet his expectations. Three main relationships are important to us Between value and value:
- Between Value and the cost of production for the consumer (Q);
- Between Value and the cost of production for the manufacturer (QP);
Between Value For the consumer and the manufacturer (K); This ratio is significant as the measure determines competitiveness Production.
Let’s look at how they changed These ratios in the process of development production in the 20th century.
Concept entrepreneurship and quality
⌠The approach to the problem is more important, than her solution” Hall’s Law.
In the entrepreneurial Activities are always present internal and external goals. Internal goals are set by the entrepreneur, starting, or developing a business. As a rule, personal – increase own income, satisfaction some personal ambitions and inclinations.
External goals of entrepreneurship – these are the goals that he expects society, allowing the entrepreneur its activities. It’s not enough for society, so that the entrepreneur only deducts he has a certain share of the profit in in the form of taxes, it is necessary for him. So that the activities of the entrepreneur helped to solve the problems that Society sets itself in front of itself.
In the most general sense, these tasks are related to the improvement of quality of life in society. Because society itself is under such quality understands. The activity of the entrepreneur is always social, and in a developed society, the entrepreneur himself is aware of this.
Philosophy entrepreneurship
He builds its activities based on philosophy entrepreneurship – concepts, describing the most general principles, approaches to the production of products and services, management of such production, the relationship between the entrepreneur, employees of the enterprise, society, the state, the natural environment. The philosophy of entrepreneurship is based on cultural and national traditions, general concepts of technical development Civilization.
The most important component part of the philosophy of entrepreneurship is a quality philosophy that also has a social focus. Let’s see how the content is determined modern quality management in accordance with the international standard ISO 8402:
“Method of management A collaborative organization of all its employees, oriented on quality and ensuring through customer satisfaction, Achieving long-term goals entrepreneurial success and benefits for all employees of the organization and the economy as a whole.”
Notes
- Note 1. ⌠ all its employees – means the entire staff of the organization, at all levels of its organizational hierarchy Structure.
- Note 2. Essential to ensure the success of this method is convinced and persistent leadership from the outside Higher Administration and Training and retraining of all workers Organization.
- Note 3. The term ⌠quality – at total quality management incorporates in itself and the achievement of all management goals.
- Note 4. ⌠Benefits for … Economy Overall – means meeting the requirements of all economic entities.
In this definition We see how they are linked into one. The whole success of the entrepreneur, the benefits for employees of the enterprise – hired employees who are not owners, – and benefits for the public economy on the whole.
Long term success
Practice shows that Only with such harmonious coordination interests of all participants in the business activities achieved sustainable Long-term success.
In modern industrialized countries at the beginning of the 20th century, a philosophy of entrepreneurship, based on the concept of the so-called “consumer societies”, i.e., societies, the purpose of which is meeting the needs of fellow citizens. Definitively, this concept of society was formulated in the 50s.
A major contribution to the realization of this the concept was brought to life by the President U.S. John Fitzgerald Kennedy, who nominated In the early 60s, the concept of the state protection of consumer rights. According to this concept, the state is obliged to actively intervene in the relationship between manufacturer of goods and services, and the consumer on the side of the latter, protecting it from poor-quality products and taking over the protection of his rights. A law on protection was passed Consumer.
The main figure of this society is the consumer. His requirements (if they are socially safe) take precedence over capabilities manufacturer and are protected by regulations states and societies.
Essential achievements of the “consumer society” can be considered:
- Consistent Putting the ideas of freedom into practice trade, which led to the creation of international market of goods and services – consumer in any country can purchase goods, produced in any country;
- The consequence of this is a sharp intensification of competition between producers, the intensification of their struggle for higher product quality and competitive prices, for reducing the timing of the release goods to the market and at the same time
- Strengthening cooperation and cooperation in production and promotion goods to the market;
- Systems development state and public protection of consumer rights on quality products and services;
- These protection systems are not only allow the consumer to collect from the manufacturer damage for poor-quality products and services. But also warn the appearance of such products on market, as well as limit monopolization of the market by the manufacturer;
- The consequence of this is the need for Manufacturer to provide Consumer
- Evidence System the quality of the goods even before how the consumer purchased this product;
Quite tall the level of self-awareness of consumers, who agree to pay for quality and are willing to cooperate with the manufacturer in its increase.
Despite all the attractiveness the concept of “consumer society”.
By the 90s. it became clear that uncontrollable an increase in needs can lead to, at least to serious violations properties of the environment, and even cause an environmental disaster.
The Earth’s resources are not designed to so that the “consumer society” enters Most of the world’s population. At the same time, the concept of development Most States have sent It is to enter the “society consumption” .
Therefore, in the near future there will be some new philosophy to develop entrepreneurship and, accordingly, A new philosophy of quality.
Individual The features of the new philosophy of quality are manifested Already now.
For example,
in the concept environmental management and in the concept Toyota production system.
Thus, in accordance with the existing philosophy entrepreneurship, completeness Product Liability and the services are the responsibility of the manufacturer. Manufacturers in different historical intervals reacted differently to this responsibility, embodying
Different Assurance Philosophies Quality.
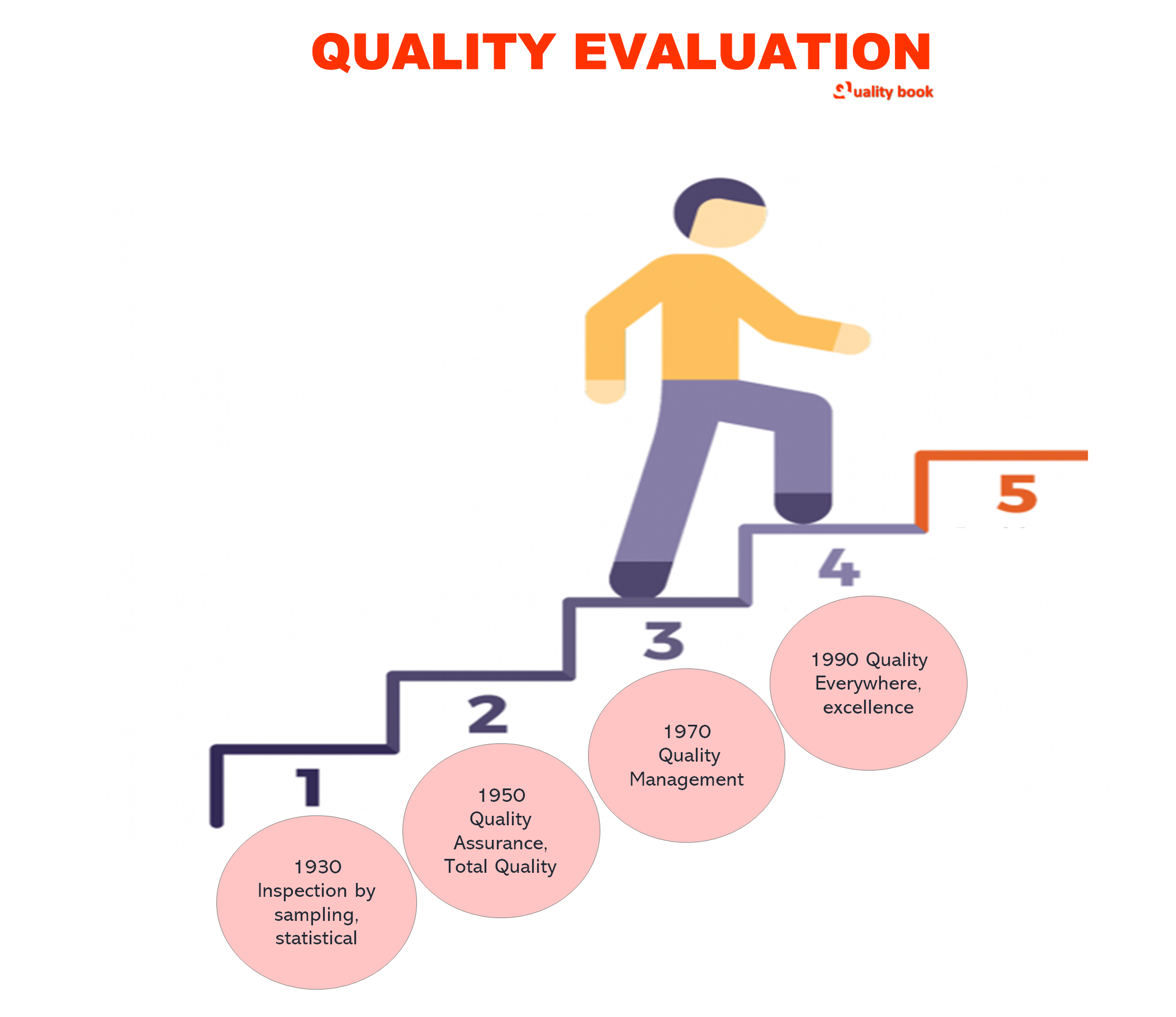
Stages of development of the philosophy of quality
⌠Products are returned, buyers – No
Robert W. Peach.
In the history of philosophy
There are 4 overlapping qualities and ongoing phases that, in full compliance with the law’s dialectics, developed under pressure contradictions between internal and external objectives of the manufacturer – quality assurance of the produced products and, accordingly, strengthening Manufacturer’s position in the market (external objective) and increased efficiency production.
That is, an increase in the company’s profits (internal goal).
This is a contradiction at every stage development of production, market and society had its own specifics and in different ways Allowed. Evolution of assurance methods qualities are shown.
 .
.
Evolution Quality Assurance Methods
Rejection phase
It started together with the craft and entered the practice of individual craftsmen who tested their own work, masters who watched the work of apprentices, buyers who carefully sorted out products to make a purchase.
We should not forget the guild organizations medieval towns that, to put it in modern terms, Certified masters – awarded the title of master after serious trials product quality. Each product was individual.
In the 70s of the XIX century in arms production (factories Samuel Colt) was born the idea of a standard quality – the products were not assembled from parts fitted to each other, and from those randomly selected from the party, that is, interchangeable parts.
Control & Rejection
These parts were inspected before assembly with the help of calibres, and the unusable ones were rejected. Control and rejection were carried out with specially trained controllers.
Outstanding contribution in the development of this phase, the American automakers – Henry Martin Leland (founder of Cadillac) and Henry Ford.
Leland used for the first time in the automotive industry work in terms of calibers and came up with a pair of “pass-through” and “non-passable” caliber.
In March 1908 British Automobile Club Experts 3 specimens were randomly selected from the export consignment of cars “Cadillac”, which arrived in England, and dismantled them to the last screw. All the details were piled up, and then some parts were removed from this pile and replaced with borrowed spare parts Again, at random at a local agency for the sale and maintenance of cars “Cadillac”.
Then a group of mechanics, armed only with screwdrivers and wrenches, assembled cars, and re-started the motors.
Two cars wound up on the first attempt, and one – with the second, and they all went for a long break-in only that the commissioned circuit Brooklands. And when the newly assembled the machines confirmed their full identity its driving characteristics parameters Factory-assembled cars, British The automobile club issued to the company “Cadillac” diploma and silver cup with the inscription “For standardization”.
Thereafter on the plate with the coat of arms of the company on cars “Cadillac” appeared the inscription “Standard of the world” is a role model for the whole world.
Ford applied assembly conveyor and introduced instead of input control of components at the assembly final control in those industries, where these components were manufactured, that is, they began to arrive at the assembly Only suitable, high-quality products.
Technical control
He also created a separate service technical control, independent from production.
Scientific synthesis and the justification of the experience gained At this stage, the work of the American scientist, engineer and manager Frederick W. Taylor, an associate of G. Ford. It was he who proposed the concept of scientific management, which included the system approach, personnel management, idea separation of responsibility between employees and managers in providing high-quality and efficient work organization, the idea of scientific rationing Labor. He developed the basic ideas of the hierarchical management structure of the organization, which in final form was formulated by Henri Fayol and Max Weber.
Can say that thanks to the activity of F. W. Taylor and G. Ford was created the concept of the organization of the machine production (production Ford-Taylor system), which basically existed to the present time and is model of organization of production of most modern enterprises. Only in the 70s it was replaced by a different concept (production Toyota system).
The basis of the concept Quality assurance of this phase can be Formulate as follows:
⌠Consumer must receive only suitable products, i.e., products that meet the standards. The main efforts should be directed to ensure that unsuitable products (marriage) would be cut off from the consumer.
Consistent Bringing this concept to life led already in the 20s to the fact that that the number of controllers in high-tech industries (aviation, military industry) began to make up to 30 – 40% of the number of production workers, sometimes more. Within this concept, quality improvement is always accompanied by an increase in the cost of its provision, i.e., the goal of increasing efficiency production and quality improvement products are contradictory (cannot be reached at the same time).
Quality Management Phase
This phase begins in the 20s of the twentieth century as an attempt if not to resolve, then to weaken the contradiction in the form peculiar to the previous one Phase. The starting point is the work, performed in the Technical Department control of Western Electric, United States. In May 1924, an employee of the department Dr. Shewhart handed over to his supervisor a short note that contained A method of now plotting diagrams known all over the world as control Shewhart maps.
Statistical methods, proposed by Schuhart, given in hand Managers tool that allowed to concentrate efforts not on how to detect and remove unusable products before they are shipped to the buyer, and on how to increase yield of suitable products in the technical process.
One of the remarkable achievements of quality management practice was the creation of an audit service in terms of quality, which, in contrast to technical control departments were engaged in not by sorting products, but by control of small samples from batches products checked the performance Quality assurance systems on Production.
The core of the concept of provisioning Qualities in this phase became:
⌠Saved The main goal is that the consumer must receive only suitable products, i.e., products that meet the standards. The rejection is saved as one of the important methods of quality assurance. But the main efforts should be focused on the management of production processes, providing an increase in the percentage of yield of suitable products.
Implementation of the concept Quality assurance in practice allowed to significantly increase efficiency production at a sufficiently high the quality of products and services that has created Conditions for the formation of a global market of goods and services.
At the same time, there was a growing understanding that everyone the production process has a certain yield limit of suitable products, and This limit is not determined by the process by themselves, but by a system, that is, the totality of activities enterprises, labor organizations, management in which this process Flows.
When this is achieved limit with a new urgency acts the same contradiction as in the previous one stages, – the goal of increasing efficiency production and quality improvement products become contradictory.
Phase Quality Management
Beginning of the management phase Qualities are usually counted from 1950 The turning point was the performance with lectures to leading industrialists Japan Dr. Edwards Deming, American. For 12 lectures, Dr. Deming met with hundreds of presenter’s managers of Japanese firms. Them, and See also Joseph M. Juran, another An American, also invited in the order of government technical aid to Japan, has been developed A program whose main idea is was:
“The basis of product quality – quality of work and quality management at all levels, i.e. Such an organization of the work of teams people, when each employee receives pleasure from my work.”
The program was based on no longer on improvement only production processes, and on improvement of the system as a whole, on the direct participation of the highest Managers of companies in problems quality, training of all employees’ companies from top to bottom main methods of quality assurance, emphasis to motivate employees to high-quality labor.
Place of the concept of avoidance defect to the consumer and the concept increasing the yield of suitable products I took the concept of “0 defects”.
It is thanks to Consistent implementation the ideas of Deming, Juran and Kaori Ishikawa Japan, a country that is more than poor natural resources and devastated war, became one of the richest Countries.
The main contribution to the development of both this phase and the subsequent one, Made.
Crosby (Crosby, Philip B.) –
in 1964 proposed program “0 defects”; Was For many years as Vice President ITT, was president of the American Quality Management Society (ASQS), currently a consultant many companies around the world, headed by consulting firm Philip Crosby Associates, Inc.
Deming (Deming W. Edwards) –
being one from the leading experts in statistical quality assurance methods, in 1950 received an invitation from the Japanese Union of Scientists and Engineers (JUSE)accept Participation in the recovery program Japanese industry.
There he is and proposed a management program quality of 14 points, developed by the principle of continuous quality improvement, who revolutionized the Japanese Industry. In his honor, JUSE In 1951 he established a very prestigious the annual prize in his name – the prize for the Japanese firm that contributed the largest Contribution to the development of management ideas quality, similar prize for foreign companies and an individual prize.
Since 1980 American Statistics Association also awards the Deming Prize. Deming was one of the most famous in the world of management consultants’ quality, author of more than 200 books in of this field, Honorary Doctor of Tens American universities.
In 1987 G. received a personal congratulation of the President of the United States. He died in 1995.
Feigenbaum (Feigenbaum Armand V.) –
developed the principles Total Quality Management and parallel (simultaneous) Engineering; He has worked for more than 10 years at General Electric, then founded own consulting firm General Systems Company, Ltd, President which is to date. This company is one of the world’s centers consulting in the field of management Quality.
Ishikawa (Ishikawa, Kaori) –
came up with a “circle of quality”, proposed cause-effect diagrams (Ishikawa diagram), developed quality management concept, in which the whole team participates Enterprise. Since the early 50s, they have taken an active part in the program JUSE in terms of quality. Appears as one From the developers of the new concept organization of production, embodied at the company “Toyota” (production Toyota system, TPS).
Juran (Juran, Joseph M.) –
developed the principle “quality triads”; is one of the leading business consultants in the field of quality.
Masing (Masing Walter) –
proposed a “handbook on quality” as the main document enterprise quality assurance systems.
We can say that It is in this phase of the provision quality management has developed in its modern sense. Contradiction Between Quality Improvement and Growth production efficiency in its the former forms were overcome – application of new management ideas allowed at the same time to increase quality and reduce production costs. Consumers in almost all countries began to receive goods and services of the highest quality at an affordable level price – the idea of a “consumer society” came true.
At the same time, the concept of standardized quality, according to which under the quality The product is understood as the product, the requirements to which he identified and fixed In the norms, the manufacturer, and the consumer has the right to either buy the proposed product, or reject it, led to exacerbate the contradiction between quality and efficiency in the new form, – in case of an error in the definition Consumer requests at the exit suitable, from the point of view of manufacturers, products on the market costs are extremely great.
Quality Planning Phase
This phase began to emerge in the mid-60s as a development idea of the previous phase in the direction of More complete satisfaction of requests Consumers. The need for development of this phase is associated with the development of the world market of goods and services, a sharp aggravation competition in this market and politics state protection of interests Consumers.
All this led to Situations where market launch products with ⌠childhood diseases or satisfying the needs of the consumer to a lesser extent than competitors’ products, On the one hand, it is related to development theories of product reliability, and on the other hand side, with the widespread introduction of computing techniques and CAD in the development process Products.
The basis of the concept of the new Phases of steel:
- the idea that the big Part of the defects of the products is laid at the development stage due to insufficient quality of design work.
- Relocation of the center the severity of the work on the creation of the product from full-scale tests of experimental samples or batches on the mathematical modeling of product properties, as well as process modeling production of products, which allows detect and eliminate design and technological defects yet before the start of the production stage;
- Place of the concept “0 defects” took the concept “satisfied consumer”;
- High Quality must be provided to the consumer for a reasonable price, which is constantly decreasing, because competition The markets are very high.
- The main ideas of the new phases are expressed in the works of Geniti Taguchi, Dr. Mitsuno, in scientific developments of the companies “Toyota” and “Mitsubishi”.
Taguchi (sometimes the spelling of Taguchi is used – Taguchi, Genichi) – suggested quality loss function, developed methodology of industrial planning Experiments.
As part of the planning phase Qualities can be practically overcome The contradiction between quality and efficiency production in its existing forms, and a new phase arises when manifestation of a new form of this contradiction. For example, consumer requirements, so that not only products, but also The production process would be environmentally friendly, i.e. would not be applied damage to the environment. At the present time time this phase is just emerging, And its concept is still final has not been formed.