The four phases of QFD (Quality Function Deployment) guide the entire cycle from product design to production, these four phases are: 1. House of Quality, 2. Technical Correlation, 3. Development, 4. Implementation. through which it is used to translate customer requirements into specific design and engineering characteristics.
This method helps in transmitting product requirements from customers to the design team as well as the production operator. Each stage has a matrix, which includes requirements for vertical columns and horizontal columns. At every stage, the path is the most important. It needs new technology, or takes a big risk, to get through to the next stage.
House of Quality
In this stage, customers help determine the needs for products or services. And it involves gathering and organizing customer requirements and determining how they relate to the product or service being developed. Also assists the research group in putting together a matrix of customer requirements. It is through this phase that different ways to meet the customer’s needs begin to be developed.
This stage is very important, as it also involves identifying the key features of the product or service and determining the trade-offs that may be necessary to meet those needs.
Technical Correlation
The transition path from the first phase becomes the requirement of this phase, in fact it is a phase of technical correlation phase. Here, the details and various components required for the manufactured product or service are determined.
The second phase involves identifying the technical characteristics and design requirements needed to meet the customer’s needs using the information gathered in the HOQ phase.
This phase also involves determining the relationships between the various technical characteristics and how they will need to be balanced to meet the customer’s needs.
The details emerging from this phase have the strongest correlation with the realization of customer-specific product requirements. They become a way of transition to the next stage.
Development
In the third step, a matrix is created to describe the process required to produce the product. This is a stage of development.
The third phase of QFD (Quality Function Deployment )involves using the information gathered in the first two phases to design and develop a product or service.
Here, it involves deciding on specific design and engineering specifications for a product or service and deciding how to implement those specifications into the final product or service.
The transition path from the second settlement becomes essential in this phase matrix. The processes at this stage will best fulfill the customer’s specific needs for the product.
At this point, the process has become the way, and the transition to the fourth stage.
Implementation
This is the implementation phase, where the fourth and final phase of QFD involves implementing the design and development decisions made in the previous phase and bringing the product or service to market.
At this stage, production requirements are formed for the production of products. A transition path from three stages becomes necessary for this stage.
This phase also includes monitoring and evaluating the performance of the product or service to ensure that it meets the customer’s needs.
The production method thus decided will enable the company to produce high quality products that meet the needs of the customers. Makes any necessary adjustments to design or engineering specifications to improve the product or service.
Example:
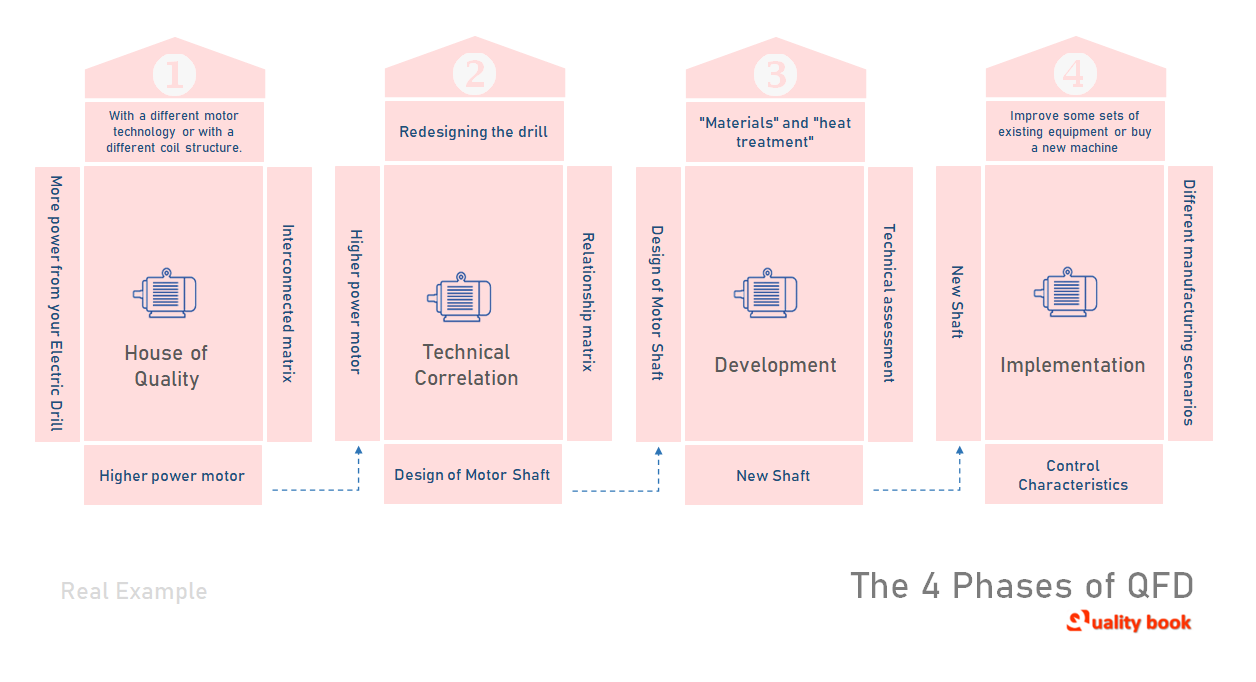
Here, we look at examples of how these four phases work. Suppose your company manufactures power tools and you find that your construction customers demand more power from your electric drill. After accepting this information. You list “more power” as the first phase requirement.
The team determined that “more power” could be achieved in three ways:
With a higher power motor, with a different motor technology or with a different coil structure. Any method used to achieve the need for “more power” is a way.
After determining the interconnected matrix, calculate the value of each mode in the relationship matrix. Piggy’s study found that a higher power motor would best meet the customer’s needs.
“High power motor” will move to the second stage of the matrix and become a requirement.
In the second phase, the team decided on important details or components of the high-power motor by creating another QFD mode.
Through technical evaluation and calculated values in the relationship matrix, the team determined that the most important component of any high-power motor design is the motor shaft itself.
Engineers participated in a technical evaluation, which helped the team realize that keeping the existing shaft would save the cost of redesigning the drill.
The “motor shaft” becomes a pathway into the matrix, transitioning to the third phase.
In the third phase, the research team measured the shaft’s ability to withstand the high torque generated by high power motors using various methods.
The research team determined that they could achieve this by using different materials and heat treatment processes. They consulted with engineers in their technical assessment to reach this conclusion. “Materials” and “heat treatment” became the way to go in matrix.
This information is then transition into Phase IV metrics.
In the fourth phase, the team decides how to make the new shaft and assemble the motor.
Two different manufacturing scenarios can be use to create a new motor assembly. Improve some sets of existing equipment or buy a new machine. Although the new machine is more expensive, the team chose the latter. Because the new machine can best meet the needs of the customer.
A major advantage of QFD is that everyone can evaluate how the solution helps meet customer needs throughout the process.
Even in the fourth stage, including the selection of production equipment. All decisions are made on the basis of meeting the customer’s needs to the greatest extent possible. When a decision is complete it should be in favor of the customer, not in engineering or manufacturing. Where the customer’s perspective is placed above the preferences of each department.
Conclusion
The four phases of Quality Function Deployment (QFD) are a systematic approach to translating customer needs and requirements into specific design and engineering characteristics for a product or service.
The four phases are: planning and data collection, product design and development, product and service delivery, and continuous improvement.
Each phase focuses on a different aspect of the product development process, with the ultimate goal of creating a product or service that meets or exceeds customer expectations.
By following the QFD methodology, companies can ensure that their products and services are design with the customer in mind, resulting in higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.